 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Published on January 31, 2024 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
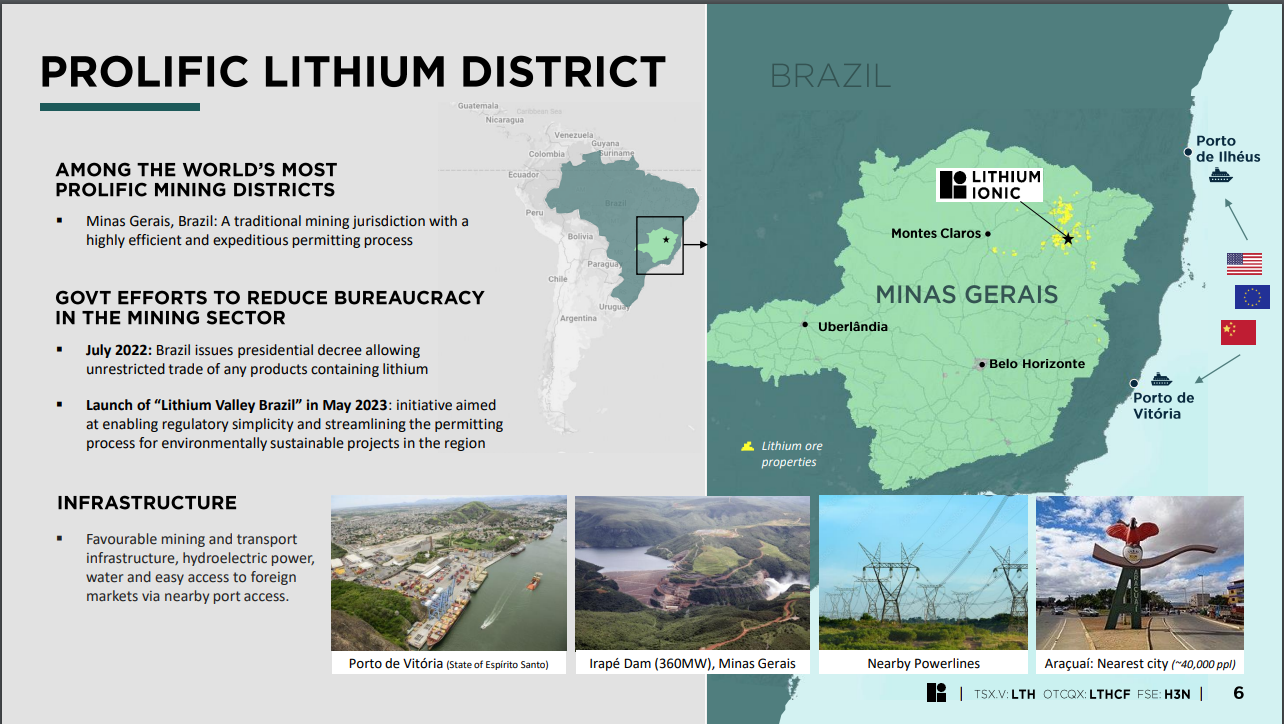
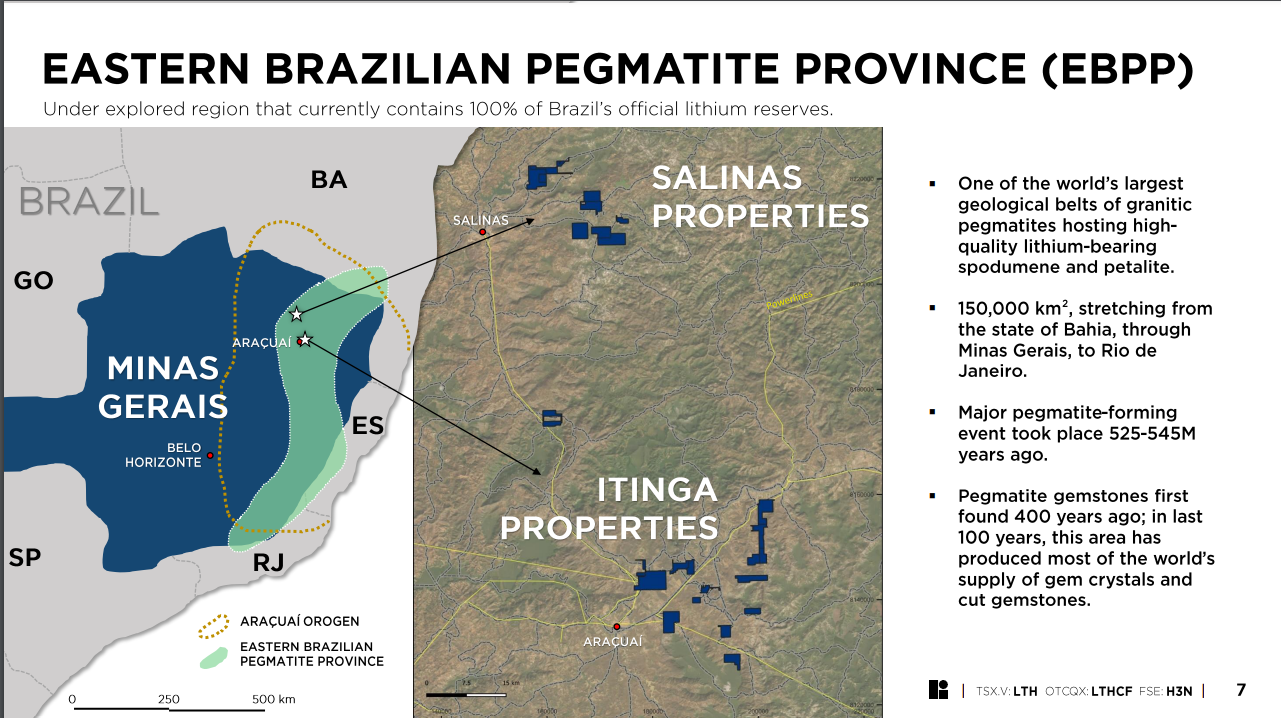
Lithium Ionic is engaged in the acquisition, exploration, and development of lithium properties in Brazil with the goal of generating long-term value for its shareholders through the discovery and potential future extraction of lithium, a critical mineral that is fueling the green revolution. The Company is currently focused on advancing its flagship Itinga and Salinas projects. Located in Minas Gerais state, Brazil, the Company’s properties span 14,182 hectares in this prolific lithium province and mining-friendly state. The Itinga Project, encompassing both the Bandeira and Outro Lado sites, is situated in the same district as Sigma Lithium Corp.’s Grota do Cirilo project, the largest lithium hard-rock deposit in the Americas, which began producing in April 2023, as well as CBL’s Cachoeira mine, which has been producing lithium since 1991. The Bandeira mineral resource for the Itinga project formed the basis of a Preliminary Economic Assessment, completed in October 2023, supporting a long-life and low-cost spodumene concentrate mining project. The Salinas Project, located approximately 100km north of the Itinga Project, is currently underway with its drilling program, with an NI 43-101 MRE expected in the near term. Brazil’s Minas Gerais state boasts excellent infrastructure, including access to highways, hydroelectrical grid power, water, and nearby commercial ports. Lithium Ionic shares began trading on the TSX Venture in May 2022 under the symbol LTH. The Company also trades on the OTCQX in the US, under the symbol LTHCF, as well as in Germany under the symbol H3N. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Disclaimer and Forward Looking Statements | ||||||||||||||||||
| Company Profile | ||||||||||||||||||
| Organizational Profile | ||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Lithium Ionic Corp. | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe nature of activities, brands, products and services |
Lithium Ionic is a Canadian junior mining company exploring and developing lithium projects in Brazil. The Company is currently focused on advancing its flagship Itinga Project, encompassing the Bandeira and Outro Lado sites, as well as the Salinas project, situated approximately 100 km north of the Itinga site. The region is known for its lithium reserves, which drive Lithium Ionic’s goal of generating value for its shareholders through the discovery and potential future extraction of lithium. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Lithium is an integral resource in the fight to decarbonize the fuel and energy industries. Lithium Ionic plans to source and develop the lithium reserves in an economical and responsible manner. Driving Lithium Ionic’s success are the following principles: safety, integrity, responsibility, accountability, and excellence. With these guiding pillars in mind, ESG actions will be integral to fulfilling the Company’s objectives. Despite Lithium Ionic being a relatively new venture, it has the potential to create long-term positive impacts by supporting local communities and contributing to the global transition to net-zero emissions through the production and distribution of commercial-grade lithium. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Link to Corporate Website | https://www.lithiumionic.com/ | |||||||||||||||||
| Industry Classification |
NAICS: 21 Mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction 212299 All other metal ore mining ISIC: B0729 Mining of other non-ferrous metal ores |
|||||||||||||||||
| Market Capitalization | $100 Million up to $1 Billion USD | |||||||||||||||||
| Type of Operations | Lithium exploration and development | |||||||||||||||||
| Company Headquarters | Toronto, Canada | |||||||||||||||||
| ESG Accountability | ||||||||||||||||||
| Role and Name of highest authority within company for Environment, Social and Governance strategy, programs and performance |
Caroline Arsenault, Corporate Communications and Investor Relations |
|||||||||||||||||
| GRI Reporting Requirements | ||||||||||||||||||
| Choose the statement as to how the organization has aligned their reporting utilizing GRI Standards |
The organization has reported in accordance with the GRI Standards for the period defined below |
|||||||||||||||||
| ESG Reporting Period | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unless otherwise noted, all data contained in this report covers the following period | ||||||||||||||||||
| From | 2023-01-01 | |||||||||||||||||
| To | 2023-12-31 | |||||||||||||||||
| External Assurance | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe your company's policy and practice for seeking external assurance, including whether and how the highest governance body and senior executives are involved | The information provided is self declared. | |||||||||||||||||
| Has the report been externally assured | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Financial Reporting Period | ||||||||||||||||||
| Does the financial reporting period align with the sustainability reporting period (eg. calendar vs fiscal) | Yes | |||||||||||||||||
| Geographic Scope of Report | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unless otherwise noted, the data in this report covers sustainability matters related to the following locations of operations | Brazil | |||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| Prolific Lithium District | Itinga and Salinas Properties | |||||||||||||||||
| Identify notable exclusions of the geographical and/or business scope of the report, and reference of any existing or planned reports that do or will address these (e.g., assets recently divested or acquired, non-managed joint ventures, specific exploration activities, recently closed sites, etc.) | None | |||||||||||||||||
| Reporting Practice | ||||||||||||||||||
| Provide the full contact details (name, title, address, email and/or phone number) for an individual responsible to address questions regarding the report or its contents |
Katrina Diez, ESG Analyst, 36 Lombard Street, Floor 4 Toronto, ON, Canada, M5C 2X3 kdiez@lithiumionic.com |
|||||||||||||||||
| Currency | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unless otherwise noted, all financial figures referenced in this report are in the following currency | CAD | |||||||||||||||||
| Membership of Associations | ||||||||||||||||||
| List of the industry associations, other membership associations, and national or international advocacy organizations in which the organisation participates in a significant role, as well as any economic, environmental, and social charters, principles, or other programmes that the organisation subscribes to or supports, such as the United Nations Global Compact (UNGC), etc. |
Lithium Ionic is compatible with all international frameworks currently incorporated within the ONYEN reporting platform. Furthermore, in the fourth quarter of 2023, Lithium Ionic initiated the IRMA's Mine Measure self-assessment for its Itinga project, with the aim of enhancing the alignment of our operations with industry best-standard practices. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Scale of the Organization | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe how the organization defines its "Operation" |
Lithium Ionic is a Canadian mining company exploring and developing its lithium properties in Brazil. Our flagship Itinga and Salinas projects cover 14,182 hectares in the northeastern part of Minas Gerais state, a mining-friendly jurisdiction that is quickly emerging as a world-class hard-rock lithium district. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of operations | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
|
This report consolidates information from our Itinga and Salinas projects, situated within 100km of one another. The Itinga project is more advanced in its development compared to the Salinas project. As a result, the predominant focus of our ESG programming is directed towards the Itinga site, which is progressing towards construction in 2024. In contrast, the Salinas site is in the early stages of exploration and development, with an ongoing drilling project currently underway. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Report the quantity of products or services provided during the reporting period and provide description (e.g. number of units produced, amount of primary commodity produced, number of services provided, etc.) | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Lithium Ionic is currently in the exploration and development phase for its project, with production not yet underway. The company is diligently advancing activities in preparation for future production phases. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Fragile and Conflict-Affected Situations | ||||||||||||||||||
| Identify all of the entity's countries of operations that align with the World Bank's list of "Fragile and Conflict-Affected Situations" | None | |||||||||||||||||
| Mineral Resource Types in Scope | ||||||||||||||||||
| Which of the following mineral resource types are covered by this report |
• Indicated • Inferred • Measured |
|||||||||||||||||
| Mineral Reserve Types in Scope | ||||||||||||||||||
| Which of the following mineral reserve types are covered by this report | None | |||||||||||||||||
|
Proven and Probable Reserves will be available when the feasibility study is completed in Q1 2024 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Strategy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Link to company's statements of: Purpose, Vision, Mission and Values; Sustainability/ESG strategy (URL) | https://www.lithiumionic.com/sustainability/ | |||||||||||||||||
| Provide a statement from the highest governance body or most senior executive of the organization (i.e., CEO, chair, or equivalent senior position) about the relevance of sustainable development to the organization and its strategy for contributing to sustainable development. (CEO's message for this report) |
Please see the attached statement from our CEO. |
|||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| CEO Statement | ||||||||||||||||||
| Material Topics | ||||||||||||||||||
| Governance of Material Topics | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe the process followed to determine the organization's material topics, including: | ||||||||||||||||||
| How did the organization identify the material topics | Other external sources, please list | |||||||||||||||||
|
In Q4 2023, Lithium Ionic established its material topics through the completion of its Environmental Control Report and an internal Materiality Assessment Questionnaire. The Environmental Control Report was submitted as a step in the application for Environmental Licensing on-site. The report provided a thorough overview of various environmental and social topics that are material to Lithium Ionic's operations. In addition to the topics identified by the report, Lithium Ionic conducted an internal Materiality Assessment. This assessment utilized GRI material topics to create a questionnaire, asking employees to rank the topics' importance. Based on the results of the questionnaire, in conjunction with the topics identified in the Environmental Control Report, we were then able to establish which material topics are most important and applicable to Lithium Ionic's operations. |
||||||||||||||||||
| How did the organization prioritize the impacts based on their significance |
The Environmental Control Report for the Itinga project, in conjunction with the GRI Standards, played a pivotal role in determining the material topics relevant to our project. Following the identification of these topics, our approach involved seeking input from our employees to gauge their perspectives on the importance of each topic to both our project and their personal priorities. Utilizing the outcomes of this questionnaire as a guiding resource, we subsequently outlined and prioritized specific topics that will be addressed in future ESG programming. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Specify the stakeholders and experts whose views have informed the process of determining its material topics and provide details |
• Employees and other workers • Local communities |
|||||||||||||||||
|
The Environmental Control Report and the material topics identified were based on a very thorough assessment of both environmental and social impacts for the projected Bandeira site. In doing so, there were consultations done with the local communities who identified areas that they would like addressed. In addition, many of our employees on-site reside in the local communities, therefore, they are able to accurately identify which material topics are important to them as both employees and local residents. This assessment, in addition to corporate-level employee assessments, helped to provide a thorough overview of the topics that are priority for our workforce and local communities. |
||||||||||||||||||
| List the organization's material topics |
• Economic Performance • Market Presence • Procurement Practices • Energy • Materials • Water • Biodiversity • Emissions • Effluents and Waste • Compliance • Transport • Overall environmental • Employment • Environmental Assessment • Environmental Grievances • Labor/Management Relations • Occupational Health and Safety • Training and Education • Diversity and Equal Opportunity • Equal Remuneration for Women and Men • Labor Practices • Grievance Mechanisms • Human Rights Investment • Non-discrimination • Freedom of Association and Collective Bargaining • Security Practices • Human Rights Grievance Mechanisms • Local Communities • Anti-corruption • Public Policy • Anti-competitive Behavior • Grievance Mechanisms for Impacts on Society • Emergency Preparedness • Closure Planning • Marketing • Communications • Materials Stewardship • Permitting • Indirect Economic Impacts |
|||||||||||||||||
| List the organization's non-material topics |
• Materials Stewardship • Customer Privacy • Product and Service Labeling • Customer Health and Safety • Artisanal and Small-scale mining • Resettlement • Supplier Assessment for Impacts on Society • Supplier Human Rights Assessment • Indigenous Rights • Forced or Compulsory Labor • Child Labor • Supplier Assessment for Labor Practices • Supplier • Products and Services |
|||||||||||||||||
| Provide reasons for considering such topics not material, provide details | Other, please specify | |||||||||||||||||
|
Lithium Ionic is currently in the exploration stage, and as such, the project has not generated any products or tailings waste, nor does it have any suppliers at this time. The Itinga Project is situated in the mining-friendly region of Minas Gerais, Brazil, known for its highly efficient permitting process. Importantly, the site is free from areas of conflict, human rights complaints, child labor, forced labor, or Indigenous occupied land. Additionally, it is not in proximity to Artisanal small-scale mining sites, and no resettlement of individuals is required. Our operations prioritize the well- being of local communities and employees, aiming for a significant positive impact on communities while minimizing environmental effects. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Report changes to the list of material topics compared to the previous reporting period | None | |||||||||||||||||
| For the top 5 material topics, the reporting organization shall report the following information: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Topic #1 | Water | |||||||||||||||||
| An explanation of why the topic is material; describe the actual and potential, negative and positive impacts on the economy, environment, and people, including impacts on their human rights |
The Itinga and Salinas projects are located within the Jequitinhonha River Basin. This location results in both positive and negative impacts on the economy, environment, and people. Positively, it holds the promise of fostering economic growth through job opportunities for the local citizens. While environmental conservation measures underscore a commitment to responsible practices. Despite these positives, challenges emerge, such as potential water resource disruption for communities along the Ribeirão Piauí near the Itinga project site and the risk of aquifer contamination. Addressing these challenges remains pivotal for ensuring sustained positive impacts and harmonizing economic development with environmental and social considerations. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Where the impacts occur |
The Salinas and Itinga projects' impacts are concentrated within the Jequitinhonha River Basin. In particular, the Itinga project is located in the sub-basin of the Ribeirão Piauí. The project's scope also reaches riverside communities along the Ribeirão Piauí, where human activity contributes to water contamination. Addressing these specific impacts is crucial for ensuring sustainable development within this distinct geographical context. |
|||||||||||||||||
| The organization’s involvement with the impacts. e.g., whether the organization has caused or contributed to the impacts, or is directly linked to the impacts through its business relationships |
The Itinga and Salinas projects' water consumption and industrial activities are integral to daily operations. Lithium Ionic plans to implement environmental control programs to mitigate the negative impacts of the project's activities, including potential aquifer contamination and disruption of water resources for communities. The organization's direct involvement in mining and industrial processes raises a responsibility to manage and mitigate the environmental and social consequences, ensuring that the proposed programs are effectively implemented to address the impacts associated with its operations. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report whether the organization is involved with the negative impacts through its activities or as a result of its business relationships, and describe the activities or business relationships | Activities | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe/provide a link to the corporate policies or commitments regarding the topic |
We do not have any corporate policies applicable to this topic at this time. However, plans to implement such as a plan will be developed as the project continues. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Explain how the organization manages the topic and actions to prevent or mitigate potential negative impacts |
As the Itinga and Salinas projects progress to construction and production scenarios, Lithium Ionic will employ several strategies to manage and mitigate potential negative impacts associated with the project. The Itinga project will emphasize responsible water usage by pumping raw water from the Ribeirão Piauí, implementing a water treatment unit, and recirculating processed water to compensate for high evaporation rates. Efforts will be made to avoid watercourse contamination, utilizing a sewage treatment plant and water and oil separator boxes for effluent disposal. The organization will also conduct environmental control programs, including the Solid and Liquid Waste Management Program, Erosive Process and Processing Effluent Control Program, and Surface Water Quality Monitoring Program. These programs will address concerns such as exposed soil in operational areas, sediment transport during the project's phases, and potential erosion caused by earthmoving activities. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe actions to address actual negative impacts, including actions to provide for or cooperate in their remediation |
To address potential negative impacts associated with the Itinga and Salinas projects, the organization will proactively implement preventative actions. The Itinga project currently has plans to establish a sewage treatment plant, water and oil separator for effluent management, and environmental control programs. In the event of soil and water quality concerns, the organization commits to cooperating in remediation efforts, ensuring that corrective measures are promptly implemented. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe actions to manage actual and potential positive impacts |
To manage both anticipated and potential positive impacts associated with the Itinga and Salinas projects, the organization will implement several strategic actions. In the realm of economic benefits, the projects will focus on contributing to regional economic growth and job creation. Environmental sustainability will be addressed through the implementation of a sewage treatment plant, water treatment unit, and various environmental control programs. These measures will aim to mitigate potential negative impacts on water quality, aquifers, and local ecosystems. By emphasizing responsible water usage, waste management, and environmental conservation, the organization will actively manage the projects' positive impacts, aligning them with principles of sustainability and responsible business practices in the future. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the processes used to track the effectiveness of the actions; |
• External auditing or verification • Impact assessments • Measurement systems • Stakeholder feedback • Benchmarking • External performance ratings |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the goals, targets, and indicators used to evaluate progress; |
The organization will focus on specific goals, targets, and indicators to assess progress. The Environmental Control Plan aims to ensure compliance with legal criteria, identify environmental needs, and assess the control system's effectiveness, including water quality. The future Monitoring and Control of Liquid and Oily Effluents Sub-Program will further evaluate system efficiency and preserve water quality, implementing measures such as treatment systems and periodic monitoring. Together, these initiatives form a comprehensive framework to ensure environmental protection throughout the project's lifecycle. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the effectiveness of the actions, including progress toward the goals and targets; any related adjustments |
We have yet to implement such measures but will measure their effectiveness as the project progresses |
|||||||||||||||||
| Lessons learned and how these have been incorporated into the organization’s operational policies and procedures | N/A. | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe how engagement with stakeholders has informed the actions taken and how it has informed whether the actions have been effective |
Stakeholder engagement has played a pivotal role in shaping the organization's response to environmental and social considerations in the project. Ongoing engagement serves as a real- time feedback mechanism to assess the effectiveness of implemented actions, and ensuring the organization remains responsive to stakeholder expectations and concerns. This collaborative approach enhances the overall effectiveness of environmental and social initiatives, aligning actions with community expectations and regulatory standards. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Topic #2 | Occupational Health and Safety | |||||||||||||||||
| An explanation of why the topic is material; describe the actual and potential, negative and positive impacts on the economy, environment, and people, including impacts on their human rights |
The topic of occupational health and safety is a crucial element of our project. On the positive side, the project promises substantial economic benefits by providing employment opportunities to a significant number of people, fostering local development, and boosting local economies. Environmentally responsible practices, such as waste management, the future Noise and Vibration Level Control Program, and the Accident Prevention and Public Health Program underscore a commitment to occupational health and safety. Potential economic costs and environmental risks necessitate strict adherence to safety measures to prevent accidents and ensure the project's long-term success. Safety protocols, including PPE and emergency plans, demonstrate a proactive approach, balancing the positive economic and environmental contributions with a commitment to worker well-being and risk mitigation. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Where the impacts occur |
The impacts of occupational health and safety will be prevalent throughout the entire project, encompassing various stages from the implementation phase to daily operational activities. These impacts will affect direct employees, contractors, and third-party workers who are employed throughout all levels of our operations. Safety measures will also extend to the project's transportation and accommodation arrangements, emphasizing the broad scope of occupational health and safety considerations. |
|||||||||||||||||
| The organization’s involvement with the impacts. e.g., whether the organization has caused or contributed to the impacts, or is directly linked to the impacts through its business relationships |
The organization will be involved in the impacts of occupational health and safety through its direct control and management of project activities. The company's decisions on transportation, accommodation, safety protocols, and adherence to labour legislation will shape the well-being and safety of the workforce. The organization will have the responsibility to ensure compliance with regulatory norms and the successful implementation of safety campaigns. Furthermore, the commitment to accessible personal protective equipment and training will underscore the organization's direct link to the impacts through its business relationships with employees. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report whether the organization is involved with the negative impacts through its activities or as a result of its business relationships, and describe the activities or business relationships | Both activities and business relationships | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe/provide a link to the corporate policies or commitments regarding the topic |
We do not have any corporate policies applicable to this topic at this time. However, plans to implement such policies will be developed. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Explain how the organization manages the topic and actions to prevent or mitigate potential negative impacts |
The organization will actively manage occupational health and safety through a comprehensive set of measures. These will include the mandatory use of PPE, regular medical examinations for all workers, risk signposting in the mine, and periodic checks on equipment. Additionally, as the project progresses and we move into a construction and production scenario, a Traffic Plan, Rescue Plan, and specific safety programs, such as the Risk Management Program and Medical Control and Occupational Health Program, will be implemented, further demonstrating a proactive approach to preventing and mitigating potential negative impacts. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe actions to address actual negative impacts, including actions to provide for or cooperate in their remediation |
Our approach to addressing actual negative impacts revolves around a strong emphasis on prevention. While our primary focus is on implementing preventive measures to ensure the well-being and safety of our workforce, we recognize the importance of continuous improvement. In the event of any accidents, we maintain a proactive stance by tracking and analyzing each incident. This analysis serves as a foundation for implementing targeted measures to address root causes and prevent the recurrence of similar incidents. Our commitment to cooperation in remediation involves actively collaborating with relevant authorities, reporting incidents, and adopting remedial actions in accordance with established protocols. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe actions to manage actual and potential positive impacts |
To manage and enhance positive impacts, the organization will implement specific programs as it moves towards a construction and production scenario. Regarding worker well- being, the provision of PPE ensures that employees are not only equipped but also trained on the correct usage of these safety measures. Proposed activities will include a detailed Work Hygiene program and Risk Management Program to establish priorities and targets for evaluation and control measures. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the processes used to track the effectiveness of the actions; |
• Internal auditing • Stakeholder feedback • Grievance mechanisms • Benchmarking |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the goals, targets, and indicators used to evaluate progress; |
The organization's goals will include maintaining compliance with regulatory norms, reducing noise levels through the future Noise and Vibration Level Control Program, and preventing accidents through safety campaigns and training. Indicators for progress evaluation will encompass noise levels, vehicle maintenance, and the effectiveness of measures to reduce occupational hazards and accidents. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the effectiveness of the actions, including progress toward the goals and targets; any related adjustments |
The aforementioned policies and plans are pending implementation into current operations, attributed to the exploratory and early nature of the project. Presently, we diligently track on-site incidents, maintaining a comprehensive record to identify any recurrent themes that necessitate further attention. As the project progresses, a phased implementation of these plans is anticipated, accompanied by ongoing assessments of their effectiveness. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Lessons learned and how these have been incorporated into the organization’s operational policies and procedures | N/A. | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe how engagement with stakeholders has informed the actions taken and how it has informed whether the actions have been effective |
Engagement with stakeholders will play a crucial role in informing the organization's actions. Feedback from workers and the community will likely influence the continuous improvement of safety measures. Periodic noise monitoring in the project area will reflect a commitment to responsiveness, ensuring that the organization adapts its actions based on the effectiveness of implemented measures and stakeholder input. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Topic #3 | Compliance | |||||||||||||||||
| An explanation of why the topic is material; describe the actual and potential, negative and positive impacts on the economy, environment, and people, including impacts on their human rights |
Legal compliance is considered a material topic for Lithium Ionic due to its significant impact on the company's operations, reputation, and stakeholder relationships. Non-compliance with Canadian and Brazilian laws and regulations could result in severe negative consequences, including legal actions, financial penalties, damage to the company's reputation, and potential disruptions to operations. On the positive side, maintaining compliance enhances the company's credibility, fosters a positive relationship with regulators and communities, and supports sustainable business practices. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Where the impacts occur |
The impacts of legal compliance are primarily felt in the areas where Lithium Ionic operates, which includes Canada and Brazil. |
|||||||||||||||||
| The organization’s involvement with the impacts. e.g., whether the organization has caused or contributed to the impacts, or is directly linked to the impacts through its business relationships |
Lithium Ionic's involvement with legal compliance impacts is direct, as it is obligated to adhere to the laws and regulations of the countries in which it operates. Lithium Ionic has had no instances of non-compliance and, therefore, has not contributed to any potential impacts. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report whether the organization is involved with the negative impacts through its activities or as a result of its business relationships, and describe the activities or business relationships | Both activities and business relationships | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe/provide a link to the corporate policies or commitments regarding the topic |
See attached for Lithium Ionic's corporate governance policies. These policies include the Code of Business Ethics and Conduct, Audit Committee Charter, and Anti-Bribery Policy. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Audit Committee Charter Code of Business Ethics and Conduct Anti-Bribery Policy |
||||||||||||||||||
| Explain how the organization manages the topic and actions to prevent or mitigate potential negative impacts |
Lithium Ionic manages the topic of legal compliance through compliance mechanisms. This includes the existence of an audit committee, ongoing financial disclosures, and the close monitoring of changes in relevant laws. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe actions to address actual negative impacts, including actions to provide for or cooperate in their remediation |
In the event of non-compliance, Lithium Ionic has established protocols for addressing negative impacts. This may involve immediate corrective actions, cooperation with regulatory authorities, and the implementation of remediation measures to rectify any harm caused. However, we have had no instances of non-compliance, and therefore, these measures have not needed to be implemented. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe actions to manage actual and potential positive impacts |
Lithium Ionic actively manages positive impacts by ensuring compliance not only with the minimum legal requirements but also by adopting best practices that contribute positively to the communities and environments in which it operates. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the processes used to track the effectiveness of the actions; |
• Internal auditing • Stakeholder feedback • Impact assessments • Measurement systems |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the goals, targets, and indicators used to evaluate progress; |
The organization establishes clear goals and targets concerning legal compliance, incorporating measurable indicators to gauge its progress. These objectives focus on maintaining a track record of zero instances of non-compliance, enhancing the organization's ability to respond promptly to regulatory changes, and continually improving overall compliance effectiveness. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the effectiveness of the actions, including progress toward the goals and targets; any related adjustments |
As a result of these actions, we have zero instances of non-compliance and plan to maintain this record throughout operations. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Lessons learned and how these have been incorporated into the organization’s operational policies and procedures |
We have learned that the strategies we are employing are effective due to our track record of meeting compliance requirements. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe how engagement with stakeholders has informed the actions taken and how it has informed whether the actions have been effective |
Lithium Ionic prioritizes engagement with key stakeholders, particularly regulatory bodies governing local, Brazilian, and Canadian legislation and regulations. Lithium Ionic is committed to strict adherence to all legal requirements and obligations. In response to any regulatory changes, we proactively stay informed to prevent compliance violations and maintain a continuous commitment to legal compliance. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Topic #4 | Local Communities | |||||||||||||||||
| An explanation of why the topic is material; describe the actual and potential, negative and positive impacts on the economy, environment, and people, including impacts on their human rights |
Community Health and Safety are material topics due to their significant impact on the well-being of local communities. Positive impacts include improved health outcomes through health investments, enhanced community relationships, and potential economic benefits. Negative impacts, if not properly managed, could result in health hazards, strained community relations, and economic downturns. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Where the impacts occur |
The impacts of Community Health and Safety initiatives are localized, directly affecting the communities in proximity to Lithium Ionic's operations. |
|||||||||||||||||
| The organization’s involvement with the impacts. e.g., whether the organization has caused or contributed to the impacts, or is directly linked to the impacts through its business relationships |
Lithium Ionic is directly involved in addressing the impacts on Community Health and Safety. The organization recognizes its responsibility to proactively identify and address the needs and concerns of local communities. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report whether the organization is involved with the negative impacts through its activities or as a result of its business relationships, and describe the activities or business relationships | Both activities and business relationships | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe/provide a link to the corporate policies or commitments regarding the topic |
See what we have implemented at the community level at our website |
|||||||||||||||||
| Sustainability Page | ||||||||||||||||||
| Explain how the organization manages the topic and actions to prevent or mitigate potential negative impacts |
To manage and prevent negative impacts, Lithium Ionic will develop a Social Communication Program. This program will enable the organization to identify and address local communities' needs and concerns effectively. Additionally, all water, waste, air, and noise/vibration programming and assessments prioritize community health and safety, ensuring that their needs are met, and safety is the priority. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe actions to address actual negative impacts, including actions to provide for or cooperate in their remediation |
In the unlikely occurrence of actual negative impacts, Lithium Ionic is unwavering in its commitment to promptly address and remediate any issues. The organization places a strong emphasis on proactive measures to prevent adverse impacts, prioritizing cooperation with stakeholders and offering the necessary support for remediation efforts if needed. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe actions to manage actual and potential positive impacts |
Lithium Ionic actively seeks to manage positive impacts on community health and safety by fostering strong relationships with local communities. This includes implementing measures that go beyond regulatory requirements to contribute positively to the well-being of communities. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the processes used to track the effectiveness of the actions; |
• Stakeholder feedback • Measurement systems • Grievance mechanisms |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the goals, targets, and indicators used to evaluate progress; |
The organization defines specific goals and targets pertaining to Community Health and Safety, emphasizing proactive measures. Key indicators include ongoing assessments of the effectiveness of health and safety programs. These evaluations are integral, incorporating community feedback and monitoring environmental factors to identify and address any potential negative impacts on the well- being of local communities. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the effectiveness of the actions, including progress toward the goals and targets; any related adjustments |
At present, our project has not caused any adverse impacts on Community Health & Safety, validating the effectiveness of our actions in achieving the intended outcomes. Nevertheless, as we transition toward a production scenario, our monitoring efforts will intensify further to consistently prioritize the well-being of local communities. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Lessons learned and how these have been incorporated into the organization’s operational policies and procedures |
Lithium Ionic has integrated lessons into its operations, emphasizing a proactive stance on Community Health and Safety. With a positive track record in the current project phase, we've learned the importance of prevention. As we transition to production, our operational policies now underscore heightened monitoring to consistently prioritize the health of local communities. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe how engagement with stakeholders has informed the actions taken and how it has informed whether the actions have been effective |
Engagement with stakeholders, especially local communities, plays a crucial role in shaping and evaluating actions. Lithium Ionic actively seeks input from communities to inform the development and effectiveness of health and safety initiatives, ensuring that the organization's efforts align with community needs and expectations. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Topic #5 | Other, please specify | |||||||||||||||||
| Business Ethics and Conduct | ||||||||||||||||||
| An explanation of why the topic is material; describe the actual and potential, negative and positive impacts on the economy, environment, and people, including impacts on their human rights |
The materiality of Business Ethics and Conduct for Lithium Ionic is evident in its significant impact on the economy, environment, and people, including human rights. Adherence to ethical standards, as outlined in the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, positively contributes to a trustworthy workplace culture, enhancing employee well-being and bolstering the local economy through stable employment opportunities. Conversely, unethical behaviour poses risks such as legal challenges and reputational damage, impacting stakeholders and the broader community. Ethical mining practices, exemplified by initiatives such as the pending IRMA self-assessment, promote environmentally sustainable and socially responsible business practices. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Where the impacts occur |
The impacts of Business Ethics and Conduct are seen across various facets of Lithium Ionic's operations. They influence the workplace culture, relationships with stakeholders, community partnerships, and the overall environmental and social sustainability of the mining activities. |
|||||||||||||||||
| The organization’s involvement with the impacts. e.g., whether the organization has caused or contributed to the impacts, or is directly linked to the impacts through its business relationships |
Lithium Ionic is actively involved in shaping the impacts of Business Ethics and Conduct. The organization's leadership, through a comprehensive Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, sets clear expectations for ethical behaviour, transparency, and accountability. This involvement extends to the implementation of policies such as the Anti- Bribery Policy and adherence to the Audit Committee Charter, ensuring that the company operates ethically and responsibly in all aspects of its business relationships. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report whether the organization is involved with the negative impacts through its activities or as a result of its business relationships, and describe the activities or business relationships | Both activities and business relationships | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe/provide a link to the corporate policies or commitments regarding the topic |
See attached link |
|||||||||||||||||
| Corporate Governance Policies | ||||||||||||||||||
| Explain how the organization manages the topic and actions to prevent or mitigate potential negative impacts |
The organization manages Business Ethics and Conduct through a proactive approach. The Code of Business Conduct and Ethics establishes a foundation for ethical behaviour, addressing areas such as abuse, violence, discrimination, illegal activities, and conflicts of interest. Additionally, the Anti-Bribery Policy and the Audit Committee Charter provide further guidance, ensuring transparency and accountability. The utilization of Onyen Corporation's ESG software enhances the efficiency of sustainability reporting, facilitating accurate and accountable reporting to regulatory bodies and international agencies. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe actions to address actual negative impacts, including actions to provide for or cooperate in their remediation |
In the event of actual negative impacts, Lithium Ionic demonstrates a commitment to addressing and remediating such issues. The organization's involvement in the IRMA self- assessment for the Itinga Project signifies a proactive stance in understanding and rectifying any misalignments with high- standard ethical mining practices. The Audit Committee and board meetings further ensure transparency and cooperation in addressing and remediating any identified issues. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe actions to manage actual and potential positive impacts |
Lithium Ionic actively manages positive impacts by integrating ESG values into its operational framework. This commitment extends to creating a positive impact on local communities, ensuring a minimal environmental footprint through sustainable practices, and prioritizing the safety and well-being of its workforce. The organization's dedication to fostering a healthy workplace environment, free from harassment and discrimination and promoting honesty and transparency underscores its commitment to long-term sustainability and social responsibility. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the processes used to track the effectiveness of the actions; |
• Internal auditing • Grievance mechanisms • Stakeholder feedback |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the goals, targets, and indicators used to evaluate progress; |
Lithium Ionic's overarching goals in the realm of Business Ethics and Conduct include fostering a workplace culture rooted in honesty, integrity, and responsibility. Key targets involve upholding the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, mitigating conflicts of interest, and ensuring ethical behaviour across all levels of the organization. Indicators for progress evaluation encompass adherence to the Anti- Bribery Policy, the effectiveness of the Audit Committee Charter, and the maintenance of a positive work environment free from discrimination and unethical practices. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the effectiveness of the actions, including progress toward the goals and targets; any related adjustments |
As of now, the effectiveness of the actions is in progress. The initiation of the IRMA self- assessment is a step toward gauging and improving ethical mining practices. Continuous adjustments, guided by insights gained through these assessments and input from our employees and stakeholders, will contribute to the ongoing effectiveness of the organization's actions. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Lessons learned and how these have been incorporated into the organization’s operational policies and procedures |
Given the commitment to continual learning, Lithium Ionic actively incorporates insights into operational policies and procedures. The ongoing self-assessment processes, combined with the commitment to transparency through the Audit Committee and board meetings, ensure that lessons learned are systematically integrated into the organization's ethical framework. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe how engagement with stakeholders has informed the actions taken and how it has informed whether the actions have been effective |
Engagement with stakeholders, including the use of ESG software and adherence to reporting standards, plays a pivotal role in shaping actions. Insights from stakeholders and employees inform adjustments and improvements to ensure the ongoing effectiveness of the organization's ethical and conduct-related actions. The commitment to openness and transparency fosters a collaborative approach with stakeholders in achieving ethical and sustainable business practices. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Supply Chain | ||||||||||||||||||
| Provide a description of the organization’s supply chain, including the types of suppliers (e.g., equipment, consumables, logistics, brokers, contractors, wholesalers, etc.) |
As an exploration and development company, our supply chain is distinct from the conventional production and supply of goods. Instead, our suppliers provide essential services crucial to the advancement of our project, notably drilling. Our drilling initiatives are executed through the engagement of three third-party companies—Foraco, Servdrill, and Geosol. These firms have been contracted by Lithium Ionic to oversee and undertake the necessary steps for our drilling programs. All personnel involved in these operations are engaged on a third-party contractor basis. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Environment | ||||||||||||||||||
| Climate Change - Stewardship | ||||||||||||||||||
| Risk Assessments | ||||||||||||||||||
| Have you identified any inherent climate-related risks with the potential to have a substantive financial or strategic impact on your business | No - not yet evaluated | |||||||||||||||||
|
At this time, we haven't conducted a climate risk assessment due to our current focus on exploration and development. However, we acknowledge the importance of climate considerations and may consider conducting an assessment in the future as part of our commitment to sustainability and risk management. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Opportunity Assessments | ||||||||||||||||||
| Have you identified any climate-related opportunities with the potential to have a substantive financial or strategic impact on your business | Other, please specify | |||||||||||||||||
|
Lithium Ionic's exploration and future production of high-grade lithium play a pivotal role in advancing the transition to a more sustainable future. A key climate mitigation strategy involves transitioning to green, renewable technologies. Lithium Ionic is contributing to this shift by identifying and eventually producing the lithium that is essential for manufacturing electric vehicle batteries and other green technologies. These batteries, in turn, contribute to the reduction of carbon emissions, playing a vital role in mitigating the effects of climate change. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | ||||||||||||||||||
| Scope 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Disclose the entity's absolute gross greenhouse gas (GHGs) emissions generated during the reporting period, expressed as metric tonnes of CO2 equivalent (tonne CO₂-e) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Carbon dioxide (CO₂) (tonne CO₂-e) | 123.499 | |||||||||||||||||
| Methane (CH₄) (tonne CO₂-e) | 0.125 | |||||||||||||||||
| Nitrous oxide (N₂O) (tonne CO₂-e) | 0.298 | |||||||||||||||||
| Hydrofluorocarbon-23 (CHF₃) (tonne CO₂-e) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Hydrofluorocarbon-32 (CH₂F₂) (tonne CO₂-e) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Sulphur hexafluoride (SF₆) (tonne CO₂-e) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Nitrogen trifluoride (NF₃) (tonne CO₂-e) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Perfluoro methane (CF₄) (tonne CO₂-e) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Perfluoro ethane (C₂F₆) (tonne CO₂-e) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Perfluoro butane (C₄F₁₀) (tonne CO₂-e) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Perfluoro hexane (C₆F₁₄) (tonne CO₂-e) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| The total amount of gross global Scope 1 GHG emissions (CO₂-e) (tonne) | 123.922 | |||||||||||||||||
|
The current tracking of our Scope 1 emissions includes the use of diesel by Lithium Ionic to power our operations. However, the current Scope 1 emissions do not cover the emissions from our third-party drilling partners. In the next reporting period, we will include any emissions incurred by our third-party drilling partners, in addition to accounting for our own diesel operations on-site. |
||||||||||||||||||
| The percentage of its gross global Scope 1 GHG emissions that are covered under an emissions-limiting regulation or program that is intended to directly limit or reduce emissions, such as cap-and-trade schemes, carbon tax/fee systems, and other emissions control (e.g., command-and-control approach) and permit-based mechanisms | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
|
Brazil does not currently have emissions- limiting regulation. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Discuss any change in its Scope 1 emissions from the previous reporting period, including whether the change was due to emissions reductions, divestment, acquisition, mergers, changes in output, and/or changes in calculation methodology (i.e. any changes the entity made to the measurement approach, inputs and assumptions during the reporting period and the reasons for those changes, if any) |
N/A. This is our first fiscal year reporting our Scope 1 emissions. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Discuss short-term, medium-term and long-term strategy or plan to manage its Scope 1 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions |
At present, our emissions predominantly come from the utilization of diesel in our exploration machinery. Anticipating a potential increase in emissions during the production stage, we recognize it is imperative to explore alternative measures to minimize our overall Scope 1 greenhouse gas emissions. This strategy aligns with our commitment to proactively address our environmental impacts and seek sustainable solutions as we progress into production. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Please discuss reduction emissions target(s) (if any) for Scope 1 in your company, and analyse the performance against the target(s) |
N/A. Presently, we do not have specific Scope 1 emissions targets, as our current emissions fall within manageable and acceptable parameters. We remain committed to ongoing monitoring and will make necessary adjustments as the project progresses. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Scope 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| If company specific calculations are not available, disclose the gross location-based energy indirect (Scope 2) global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions to the atmosphere (tonne CO₂-e): | ||||||||||||||||||
| Does the company purchase externally supplied energy (grid electricity) | Yes | |||||||||||||||||
| Report the total electricity purchased from external suppliers for the reporting year in gigajoules (GJ) | 165.766 | |||||||||||||||||
| In what jurisdiction is the source of energy (utility) located | Brazil | |||||||||||||||||
| Conversion factor (see Guidance): | 0.362 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total amount of Scope 2 GHG emissions from purchased electricity (CO₂-e) (tonne) | 16.669 | |||||||||||||||||
| Does the company purchase externally supplied heat | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Does the company purchase externally supplied steam | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Does the company purchase externally supplied cooling | No | |||||||||||||||||
| The total amount of gross global Scope 2 GHG emissions (CO₂-e) (tonne) | 16.669 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total amount of Scope 2 GHG emissions (CO₂-e) that are covered under emissions-limiting regulations (tonne) for the jurisdiction in which the company is working. | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Brazil does not currently have emissions- limiting regulations |
||||||||||||||||||
| Percentage of its gross global Scope 2 GHG emissions that are covered under an emissions-limiting regulation or program that is intended to directly limit or reduce emissions, i.e., cap-and-trade schemes, carbon tax/fee systems, and other emissions control (e.g., command-and-control approach) and permit-based mechanisms | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Discuss long-term and short-term strategy or plan to manage Scope 2 emissions, emissions reduction targets, and an analysis of performance against those targets |
We are committed to securing hydroelectric power from the Irape Dam for our on-site electrical operations. This deliberate choice forms a crucial part of our strategy to significantly reduce our Scope 2 emissions across all operational phases. Furthermore, we are pleased to announce the successful partnership agreement with CEMIG for the construction of hydroelectric grid infrastructure for the Bandeira Site. This strategic initiative not only enhances our commitment to sustainable practices but also reinforces our dedication to integrating clean energy solutions into our operational framework. The forthcoming hydroelectric grid hookup marks a significant milestone in our pursuit of environmental responsibility and aligns with our broader sustainability objectives. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Please discuss reduction emissions target(s) for Scope 2 (if any) in your company, and analyse the performance against the target(s) |
At present, while we do not have specific Scope 2 emission targets, we anticipate a reduction of Scope 2 emissions throughout the project. This expectation is attributed to the availability of hydroelectric infrastructure in the region. We will maintain continuous monitoring of total greenhouse gas emissions, enabling us to assess and identify areas within our operations that may require reevaluation and adjustments as the project progresses. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Scope 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Is the Organization disclosing gross "other indirect" global Scope 3 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions to the atmosphere of the seven GHGs covered under the Kyoto Protocol (tonne CO₂-e)? These emissions are not included in Scope 2 and occur outside of the organization including both upstream and downstream emissions, e.g., transporting fuel to market, or transporting fuel to the plant or site to create your product, or transporting your product to market | No | |||||||||||||||||
|
At this early stage of the project, we are not presently monitoring Scope 3 emissions. As the project progresses, we will assess the scope and nature of our activities, and consider the potential inclusion of Scope 3 emissions based on the project's development and requirements. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Air Emissions | ||||||||||||||||||
| Report emissions of air pollutants that are released into the atmosphere | ||||||||||||||||||
| Emissions of carbon monoxide, reported as CO (tonne) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
|
At present, Lithium Ionic focuses exclusively on monitoring greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions stemming from our diesel-dependent exploration equipment, and our electrical usage. Records for other supplementary air pollutants are not presently maintained, given the limitations of the current operational phase in tracking emissions from our machinery. We recognize a comprehensive assessment of these additional air emissions is crucial for a holistic understanding of Lithium Ionic's environmental impact. As our project advances, we are actively exploring strategies to incorporate monitoring of these supplementary air pollutants. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Energy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Energy Consumption | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total energy consumption within the organization | 195.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Report the energy owned and controlled by the organization consumed in gigajoules for the following | 195.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Electricity purchased/generated for consumption (gigajoules, GJ) | 195.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Heating purchased/generated for consumption (gigajoules, GJ) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Cooling purchased/generated for consumption (gigajoules, GJ) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Steam purchased/generated for consumption (gigajoules, GJ) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Non-renewable fuel consumed (gigajoules, GJ) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Renewable fuel consumed (gigajoules, GJ) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Energy Management | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total energy consumed in aggregate, in gigajoules (GJ) (hydrocarbons and electricity) including the fuel types used (e.g., biomass, hydro-electric power or bioenergy) | 195.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Percentage energy consumed that was supplied by grid electricity | 100.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percentage of energy consumed that is renewable energy (does not include purchased grid-mix) | 100.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Water | ||||||||||||||||||
| Reuse and recycle | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total volume of water that has been used in an operational task and is recovered and used again in an operational task, either without treatment (reuse) or with treatment (recycle) (megalitres) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
|
At present, we do not engage in recycling or reusing water utilized in operational tasks. As outlined in our recently submitted Environmental Control Report, we recognize the importance of addressing sustainable water management. Consequently, establishing a water recycling program is a priority for our environmental programming as the project advances. This initiative aims to significantly reduce our overall water consumption and minimize our water footprint. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Water Management | ||||||||||||||||||
| Disclose the amount of freshwater water that was consumed in its operations (in thousands of cubic meters) | 1.284 | |||||||||||||||||
| Analyse and list all operations for water risks and identify activities that withdraw and consume water in locations with High (40–80%) or Extremely High (>80%) Baseline Water Stress as classified by the World Resources Institute’s (WRI) Water Risk Atlas tool, Aqueduct |
Our operations are situated in areas that are not classified as High or Extremely High Water Risk according to the World Resources Institute's (WRI) Water Risk Atlas tool. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Disclose the freshwater withdrawn in locations with High or Extremely High Baseline Water Stress as a percentage of the total water withdrawn | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Disclose freshwater consumed in locations with High or Extremely High Baseline Water Stress as a percentage of the total water consumed | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Total water consumed in locations with high or extremely high baseline water stress (in thousands of cubic meters) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of incidents of non-compliance associated with water quality permits, standards, and regulations, including violations of a technology-based standard and exceedances of quality-based standards (note: only those that resulted in a formal enforcement action(s)) | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
|
We have had no instances of non-compliance related to water quality permits, standards, or regulations, including violations of technology- based standards and surpassing quality-based standards. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Waste Management | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tailings Storage Facilities Management | ||||||||||||||||||
| Does your company manage Tailings Storage Facilities | No | |||||||||||||||||
|
At present, tailings are not generated, given the early exploration phase of the project. However, in preparation for future production, considerations for tailings site selection and development are in progress, ensuring that proper precautions will be implemented on-site to guarantee safety. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Disclose the approach to the development of Emergency Preparedness and Response Plans (EPRPs) |
We are in the process of developing an emergency evacuation plan, which will be implemented as we transition into a construction and production scenario. Upon completion, the plan will be communicated to all employees and integrated into our safety training programs. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Innovation | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe nature of spending on Research, Development and Technologies for waste management compliance and improvement |
At present, we are actively exploring avenues for recycling our non-hazardous waste, with a specific emphasis on redirecting such waste to support agricultural activities and municipal projects. Additionally, we are implementing waste segregation practices across our operations at administrative sites. Currently, waste segregation is in place at our head office, and we have plans to expand this initiative throughout our operations. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Biodiversity | ||||||||||||||||||
| Management Plan | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe the environmental and biodiversity management plan(s) implemented at active sites |
Currently, Lithium Ionic does not have established environmental and biodiversity plans. However, our Environmental Control Report outlines a series of programs and plans, encompassing vegetation suppression and flora and fauna conservation, which will be implemented as we progress towards a construction and production scenario. Furthermore, in 2024, we intend to establish an ESG strategy that will incorporate biodiversity management as a key component. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 1.1 Lifecycle stages to which the plan(s) apply |
• Exploration and appraisal • Production • Site development • During closure |
|||||||||||||||||
|
At present, we do not have a biodiversity management plan in place. However, as outlined in our Environmental Control Report, future programming related to biodiversity management will be implemented across multiple project stages, encompassing exploration and appraisal, site development, production, and closure. |
||||||||||||||||||
| 1.2 The topics addressed by the plan(s) | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||
| 1.3 The underlying references for its plan(s), including whether they are codes, guidelines, standards, or regulations; whether they were developed by the entity, an industry organization, a third-party organization (e.g., a non-governmental organization, a governmental agency, or some combination of these groups) |
The basis for future initiatives is based on insights drawn from our Environmental Control Report. The identified topics in the report will guide us in addressing specific environmental areas that require attention throughout our operations. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Impacts | ||||||||||||||||||
| Does access to the site involve traversing a protected area | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Do any of the entities concessions share a watershed with a protected area | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Provide context and description of site access involving traversing protected areas, and/or watersheds shared with a protected area. Include reference to measures in place to assure access, any proactive programs to support the biodiversity of the protected area, and any formal complaints or compliance issues and related steps to resolve |
Brazil’s Minas Gerais state boasts excellent infrastructure, including highway access, hydroelectrical grid power, water, and nearby commercial ports. To gain access to the Itinga Project, there is no need to traverse any protected areas. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Percentage of proved reserves in sites with protected conservation status or in areas of endangered species habitat | Does Not Apply | |||||||||||||||||
| Percentage of probable reserves in sites with protected conservation status or in areas of endangered species habitat | Does Not Apply | |||||||||||||||||
| Social | ||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Employees Information | ||||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of direct employees by employment type (permanent and temporary), by gender | 54 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of permanent employees | 54 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of permanent employees - Female | 12 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of permanent employees - Male | 42 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of temporary employees | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of temporary employees - Female | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of temporary employees - Male | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of non-guaranteed hours for direct employees by gender | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of non-guaranteed hours for female employees | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of non-guaranteed hours for male employees | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of direct employees by employment type (full-time and part-time), by gender | 54 | |||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of full-time employees | 54 | |||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of part-time employees | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of full-time employees - Female | 12 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of part-time employees - Female | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of full-time employees - Male | 42 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of part-time employees - Male | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe the methodologies and assumptions used to compile the data |
This data was obtained from our corporate accountant and on-site HR coordinator. Our organization consists of both full-time employees and contractors. According to Brazilian labor laws, there are two contract types: CLT and PJ. CLT contracts represent full- time salaried employees, whereas PJ contracts resemble a contractor employment relationship. For the purpose of this report, all CLT employees will be categorized as 'Direct Employees,' while PJ contracts will be classified as 'Workers who are not employees.' Furthermore, all employees at the corporate level are engaged on a contractor basis and will also be included in the 'Workers who are not employees' category. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Are the numbers reported in head count, full-time equivalent (FTE), or using another methodology | Reported in head count | |||||||||||||||||
| Are the numbers reported at the end of the reporting period, as an average across the reporting period, or using another methodology |
The numbers are reported at the end of the reporting period |
|||||||||||||||||
| Provide contextual information necessary to understand the direct employment information provided |
All our corporate employees operate on a full- time contractor basis. Consequently, our elevated contractor ratio is attributed to the significant presence of contractors at both the corporate and on-site levels. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Workers Who are Not Employees | ||||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of workers who are not employees and whose work is controlled by the organization | 59 | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe the most common types of worker and their contractual relationship with the organization |
The workers considered in this classification are those engaged as contractors for Lithium Ionic. A predominant portion of our workforce operates as contractors, given that the majority of both our corporate and on-site teams work under full-time contractor employment contracts. Hence, the notable proportion of 'workers who are not employees' is a reflection of our distinctive workforce employment composition. |
|||||||||||||||||
| The type of work they perform |
At the corporate level, all contractors are tasked with communicating Lithium Ionic's projects and progress to the capital markets. On-site, contractors fulfill diverse roles, including field assistants, field prospectors, and general service assistance. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of workers who are not employees by employment type (full-time and part-time) and by gender | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of full-time workers who are not employees - Female | 12 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of part-time workers who are not employees - Female | 8 | |||||||||||||||||
|
The female part-time workers who are not direct employees are our corporate contractors. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of full-time workers who are not employees - Male | 38 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of part-time workers who are not employees -Male | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe the methodologies and assumptions used to compile the information about workers who are not employees. |
The information pertaining to contractors was gathered from on-site sources, documents, and our corporate accountant. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Is the number of workers who are not employees reported in head count, full-time equivalent (FTE), or using another methodology |
The count of 'workers who are not employees' is reported in terms of headcount. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Is the number of workers who are not employees reported at the end of the reporting period, as an average across the reporting period, or using another methodology |
The number of workers who are not employees is reported at the end of the reporting period. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Scale of the Organization | ||||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of direct employees (exclude workers who are not employees) | 54 | |||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of male direct employees (exclude workers who are not employees) | 42 | |||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of female direct employees (exclude workers who are not employees) | 12 | |||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of workers who are not employees whose work is controlled by the organization | 59 | |||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of workers who are not employees - Female | 20 | |||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of workers who are not employees - Male | 39 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total employed workforce (include direct employees and workers who are not employees) | 113 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total employed female workforce (include direct female employees and female workers who are not employees) | 32 | |||||||||||||||||
| Female workforce as percentage of total employed workforce | 28.3186% | |||||||||||||||||
| Total employed male workforce (include direct male employees and male workers who are not employees) | 81 | |||||||||||||||||
| Male workforce as percentage of total employed workforce | 71.6814% | |||||||||||||||||
| Workers who are not employees (contractors) as percentage of total employed workforce | 52.2124% | |||||||||||||||||
| Turnover | ||||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number and rate of turnover for all Direct Employees | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of turnover (the number that left during the period) | 4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Rate of turnover - direct employees | 11.1111% | |||||||||||||||||
| Turnover & Gender Breakdown | ||||||||||||||||||
| Female direct employees | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of turnover (the number of females that left during the period) | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Rate of turnover, females | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Male direct employees | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of turnover (the number of males that left during the period) | 4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Rate of turnover, males | 14.2857% | |||||||||||||||||
| Turnover & Age Breakdown | ||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Employees aged 30 years old and under | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of turnover (the number that left during the period) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| As percent of total direct employees | 62.9630% | |||||||||||||||||
| Rate of turnover | 4.3478% | |||||||||||||||||
| Direct Employees aged between 30 and 50 years old | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of turnover (the number that left during the period) | 3 | |||||||||||||||||
| As percent of total direct employees | 101.8519% | |||||||||||||||||
| Rate of turnover | 7.3171% | |||||||||||||||||
| Direct Employees over 50 years old | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of turnover (the number that left during the period) | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| As percent of total direct employees | 42.5926% | |||||||||||||||||
| Rate of turnover | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Identify types of employees captured in the turnover rate calculations |
• All employees on the payroll • Full-time-equivalent only |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Our turnover calculations encompass both full- time direct employees and contractors at both the on-site and corporate levels. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Average age of direct employees | 43 | |||||||||||||||||
| Diversity and Equal Opportunity | ||||||||||||||||||
| Diversity of Governance Bodies | ||||||||||||||||||
| Report the percentage of the diversity categories for the highest governance body and the total workforce per employee type | ||||||||||||||||||
| Board of Directors | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total Board of Directors | 8 | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Male | 75.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Female | 25.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Non-Binary | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Gender not disclosed | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent under 30 years of age | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent between 30 and 50 years of age | 25.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent over 50 years of age | 75.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent minority or vulnerable group individuals in the "Board of Directors" category | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Diversity of Direct Employees | ||||||||||||||||||
| Senior Management | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total Senior Managers | 7 | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Male | 100.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Female | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Non-Binary | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent of gender not disclosed | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent under 30 years of age | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent between 30 and 50 years of age | 57.1429% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent over 50 years of age | 42.8571% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent of minority or vulnerable group individuals in the "Senior Management Employee" category | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Salaried (excluding Senior Management) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total Salaried (excluding Senior Management) | 53 | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Male | 77.3585% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Female | 22.6415% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Non-Binary | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Gender not disclosed | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent under 30 years of age | 39.6226% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent between 30 and 50 years of age | 52.8302% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent over 50 years of age | 5.6604% | |||||||||||||||||
| Technical Employees (skilled hourly) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total Technical Employees | 43 | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Male | 72.0930% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Female | 27.9070% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Non-Binary | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent Gender not disclosed | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent under 30 years of age | 18.6047% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent between 30 and 50 years of age | 58.1395% | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent over 50 years of age | 23.2558% | |||||||||||||||||
| Diversity of Workers Who Are Not Employees | ||||||||||||||||||
| Workers who are not employees | ||||||||||||||||||
| Labour Relations | ||||||||||||||||||
| Collective Bargaining Agreements | ||||||||||||||||||
| Percentage of total direct employees covered by collective bargaining agreements | 0.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| For direct employees not covered by collective bargaining agreements, report whether the organization determines their working conditions and terms of employment based on collective bargaining agreements that cover its other employees or based on collective bargaining agreements from other organizations |
We presently do not have a collective bargaining agreement in place. This decision is reflective of our organizational structure and the current state of our workforce dynamics, which have not indicated the necessity for such an agreement. We remain open to dialogue and collaboration with our employees, and any future considerations for a collective bargaining agreement will be thoroughly assessed in alignment with the evolving needs and conditions of our workforce. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Notice Periods | ||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum number of weeks’ notice typically provided to direct employees in the active workforce and their representatives prior to the implementation of significant operational changes that could substantially affect them | 12 | |||||||||||||||||
|
The notice period for officers/directors is set at 12 months, while other contractors are subject to a 3-month notice period. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Occupational Health and Safety | ||||||||||||||||||
| Work-related Injuries | ||||||||||||||||||
| Injuries - For the total workforce | ||||||||||||||||||
| Number of fatalities as a result of work-related injury | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Rate of fatalities resulting from work-related injury. Note: calculating per 200,000 hours worked | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of high-consequence work-related injuries (excluding fatalities) | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Rate of high-consequence work-related injuries (excluding fatalities) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of recordable work-related injuries | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Rate of recordable work-related injuries | 1.781 | |||||||||||||||||
| Main types of work-related injury, e.g., confined space, trips, falls, etc |
The primary reported work-related injuries encompass minor cuts, scrapes, and minor collisions involving vehicles. It is important to note that none of these incidents resulted in severe injuries. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Number of hours worked | 112,320 | |||||||||||||||||
| Injuries - workers who are not employees, but whose work and/or workplace is controlled by the organization | ||||||||||||||||||
| Number of fatalities as a result of work-related injury | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Rate of fatalities resulting from work-related injury. Note: calculating per 200,000 hours worked | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of high-consequence work-related injuries (excluding fatalities) | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Rate of high-consequence work-related injuries (excluding fatalities) | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of recordable work-related injuries | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Rate of recordable work-related injuries | 1.797 | |||||||||||||||||
| Main types of work-related injury, e.g., confined space, trips, falls, etc |
The same risks identified as potential risks for direct employees also apply to "workers who are not employees but whose work is controlled by the organization." |
|||||||||||||||||
| Number of hours worked | 111,280 | |||||||||||||||||
| Combined (Employees and non-employees, but controlled by the organization): | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total Hours Worked | 223,600 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of all work-related injuries | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| Rate of work-related injuries | 1.789 | |||||||||||||||||
| Report the work-related hazards that pose a risk of high-consequence injury, including | ||||||||||||||||||
| How have these hazards been determined |
The site is situated in a dry semi-arid climate that allows for year-round operations. However, this climate is characterized by very hot temperatures, particularly in the summer months, which can pose a risk for employees. Fortunately, all on-site employees are local residents and are well-acquainted with the climate-related risks, enabling them to navigate these conditions effectively. Operational risks associated with equipment usage are also recognized. Each employee undergoes comprehensive training on how to operate machinery safely, and precautionary measures are emphasized. Our Safety Dialogue further facilitates shared learning among employees, promoting a culture of continuous improvement and adherence to safety protocols. In addition, our Environmental Control Report has identified potential hazards for employees, allowing us to proactively implement preventive measures and mitigation strategies to avert accidents. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Which of these hazards have caused or contributed to high-consequence injuries during the reporting period | None | |||||||||||||||||
| Actions taken or underway to eliminate these hazards and minimize risks using the hierarchy of controls |
Our on-site team actively engages in a Daily Safety Dialogue, during which employees report any near accidents. This open communication platform allows us to promptly identify potential risks, enabling us to assess whether additional training is required or if further prevention mechanisms need to be implemented. This proactive approach supports our commitment to continuously enhance safety measures and maintain a secure working environment. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report on actions taken or underway to eliminate other work-related hazards and minimize risks using the hierarchy of controls |
We conduct a Daily Safety Dialogue as part of our safety protocols, facilitated by an on-site safety technician. This dedicated professional is responsible for tracking all injuries and ensuring that operational activities prioritize safety. This proactive approach underscores our commitment to maintaining a secure working environment. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Whether and, if so, why any workers have been excluded from this disclosure, including the types of worker excluded, e.g., short-term contractors |
We exclusively document injuries sustained by our direct employees and contractors in our records, excluding any injuries incurred by third-party workers involved in our operations. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Disclose any contextual information necessary to understand how the data have been compiled, i.e., any standards, methodologies, and assumptions used |
Our Operational Safety Technician on-site maintains and documents all recordable injuries in our records. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Safety Training | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe any occupational health and safety training provided to workers, including generic training, as well as training on specific work-related hazards, hazardous activities, or hazardous situations |
At present, training is conducted as a general onboarding introduction to familiarize employees with their specific roles. Highly technical roles, occupied by third-party workers, involve training provided by their respective employers. Recognizing the need for a more standardized approach, Lithium Ionic is in the process of creating a schedule to incorporate additional mandatory training as an integral part of standard operations for all Lithium Ionic employees. This initiative will be progressively implemented, ensuring that as more employees are hired during the construction and production phases, they will undergo the necessary mandatory training to uphold the highest safety and operational standards. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Security, Human Rights and Rights of Indigenous People | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe the nature of any social risks, for all operating countries, that could have a material impact on the operations |
The Minas Gerais State in Brazil, along with surrounding cities and communities, actively supports the development of the region for mining, aiming to boost economic growth and job creation. Our operations closely collaborate with local entities, adhering to all social and legal requirements. To date, there have been no instances of social risks throughout our operations, and we foresee no challenges in the future. Moreover, we have conducted surveys in local communities, seeking input on the project, and no issues have been identified by local residents. This proactive engagement reflects our commitment to transparent communication and community involvement in our endeavors. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Percentage of proved reserves that are located in or near areas that are considered to be indigenous peoples’ land | Does Not Apply | |||||||||||||||||
|
We are not located in any areas that are considered to be Indigenous peoples' land |
||||||||||||||||||
| Which indigenous rights of communities in which the entity operates or intends to operate are respected, provide a description of the entity's due diligence practices and procedures in the details. | Other, please specify | |||||||||||||||||
|
There are no Indigenous Communities located near or on our site, however we respect and consult the local communities near our operations. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Which human rights procedures the entity's due diligence practices include, provide description in the details | Other, please specify | |||||||||||||||||
|
Lithium Ionic has a zero-tolerance policy when it comes to discrimination, harassment, or violence. The company adheres to a strict Code of Business Conduct and Ethics. In addition, Lithium Ionic believes that sustainable mining practices have a direct impact on the host country. Therefore, we strive to ensure that our activities have minimal disruptions on the residents of our Project’s neighbouring cities (Itinga and Araçuaí). |
||||||||||||||||||
| Discuss the practices and procedures while operating in areas of conflict, describing the approach according to the Five-Step Framework outlined in the OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains of Minerals from Conflict-Affected and High-Risk Areas | N/A. We do not operate in any areas of conflict | |||||||||||||||||
| Community Relations | ||||||||||||||||||
| Discuss the processes, procedures, and practices to manage risks and opportunities associated with the rights and interests of communities in areas where it conducts business |
Lithium Ionic is committed to fostering strong relationships with local communities throughout all phases of its operations. We prioritize the hiring of local talent and sourcing from nearby suppliers, allocating 65% of our procurement spending to local sources. As the project advances, we plan to expand our community programming, enhance existing infrastructure, and increase community investment. In 2023, Lithium Ionic solidified its commitment to local employment by signing a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with "Invest Minas." This agreement underscores our dedication to prioritize local talent in our hiring practices. Additionally, our proactive engagement includes surveys in local communities to gather input on the project. This reflects our unwavering commitment to transparent communication and community involvement in all our endeavors. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Programs | ||||||||||||||||||
| Report on community relations programs, objectives and achievements in the past 3 years |
Lithium Ionic is developing an action plan in collaboration with the two closest communities and the municipalities. This plan includes strategic partnerships with local public authorities and entities already operating in the region to address community needs and provide occasional services based on demand. As a demonstration of our commitment to community well-being, we've donated five months' worth of oxygen to St. Vincent Hospital and initiated a project to construct a bridge in José Gonçalves, Araçuaí, enhancing community accessibility. Furthermore, plans are underway to contribute to the renovation of two churches in the Barreiro Community and the Barra da Barriguda community. Our dedication to community engagement extends to job creation, aiming to provide employment opportunities to local citizens. The majority of our on-site team resides within the local communities, contributing to the improvement of local economies and fostering a positive impact through our project. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Risks and Opportunities | ||||||||||||||||||
| Disclose the total number of site shutdowns or project delays due to non-technical factors | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Disclose the total aggregate duration (in days) of site shutdowns or project delays due to non-technical factors | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Governance | ||||||||||||||||||
| Governance structure and composition | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe the governance structure, including committees of the highest governance body (e.g. the Board of Directors, the Executives, the Board Environment Committee, Board Safety Committee, the Advisory Committee, etc.) |
The governance structure of Lithium Ionic comprises a senior management team, a Board of Directors, and an Audit Committee. The senior management team consists of six members, the Board of Directors consists of eight members, and the Audit Committee is appointed by the Board, as specified in the Audit Committee Charter 2021. |
|||||||||||||||||
| List the committees of the highest governance body that are responsible for decision making and overseeing the management of the organization’s impacts on the economy, environment and people (e.g. Board level Environment Committee, Safety Committee, ESG Committee, Advisory Committee, etc.) |
The Board of Directors and CEO at Lithium Ionic are fully aware of potential impacts on the economy, environment, and people. We adhere to a rigorous approach, ensuring that no actions or projects are implemented without thorough consideration of the potential impacts these decisions could cause. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Delegation of responsibility for managing impacts | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe whether the highest governance body has appointed any senior executives with responsibility for the management of organization’s impacts on the economy, environment and people (e.g., is it part of the Governance structure of the company, CEO's role, CFO's role, Sustanability Executive, etc.) |
The company has not designated a specific senior executive exclusively responsible for the company's ESG matters. However, an ESG Analyst is in place, responsible for overseeing ESG initiatives and progress. The ESG Analyst reports directly to senior executives, providing regular updates on ESG matters and contributing to the integration of environmental, social, and governance considerations within the company's overall strategy. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Policy commitments | ||||||||||||||||||
| Provide a description of the organization’s policy commitments for responsible business conduct |
At Lithium Ionic, our management team is committed to leading by example, fostering a culture of trust and transparency. The company's governance framework emphasizes honesty, integrity, fairness, and responsibility in its operations. To reinforce these principles, Lithium Ionic adheres to a rigorous Code of Business Conduct and Ethics. This code serves as a comprehensive guide, ensuring that all individuals associated with the company adhere to the highest standards. It outlines the company's rules and expectations regarding issues such as abuse, violence, discrimination, illegal activities, conflicts of interest, and unethical behavior, setting a clear standard for ethical conduct across all aspects of the organization. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Code of Business Conduct and Ethics | ||||||||||||||||||
| What are (if any) the authoritative intergovernmental instruments that the commitments reference |
At Lithium Ionic, we establish the foundation for human rights protections by adhering to established legislation, including the UN Declaration of Human Rights. Our commitment extends to complying with legal requirements and employment standards in both Canada and Brazil. By aligning with these recognized frameworks, we ensure the promotion and protection of human rights across all stages of our operations. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Do the commitments stipulate conducting due diligence | Yes | |||||||||||||||||
|
Although we do not have a third-party auditor for our ESG commitments, we do have an Audit Committee for all financial corporate operations. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Do the commitments stipulate applying the Precautionary Principle or Approach (see instructions). | Yes | |||||||||||||||||
|
Lithium Ionic's Environmental and Social Impact Assessment is currently underway. We are awaiting the results of the assessment in order to make informed decisions regarding project expansion and future developments. Meanwhile, the recently submitted Environmental Control Report outlines a series of precautions and programs that will be implemented before production begins. Our commitment to minimizing environmental impact is paramount, and every decision takes into account its effects on the surrounding areas, both environmentally and socially. This remains a fundamental aspect of our operations and will continue to be an essential consideration as the project progresses. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Do the commitments stipulate respecting human rights | Yes | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe the specific policy commitment to respect human rights |
Lithium Ionic maintains a zero-tolerance policy towards discrimination, harassment, or violence within its operations. This commitment is reinforced through a strict Code of Business Conduct and Ethics. Furthermore, the company acknowledges the direct impact of mining practices on the host country and, accordingly, strives to minimize disruptions to the residents of neighboring cities, namely Itinga, Araçuaí, Barreiros Community, and Fazenda Velha Community as part of our broader commitment to responsible and sustainable practices. |
|||||||||||||||||
| What are (if any) the internationally recognized human rights that the commitment covers | We protect all human rights within operations. | |||||||||||||||||
| Provide links to the policy commitments, if publicly available, or, if the policy commitments are not publicly available, explain the reason for this | See attached link | |||||||||||||||||
| Corporate Governance Policy Commitments | ||||||||||||||||||
| Report the level at which each policy commitment was approved within the organization, including whether this is the most senior level |
Our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics extends to all levels within the organization. |
|||||||||||||||||
| To what extent the policy commitments apply to the organization’s activities and to its business relationships |
Lithium Ionic's policy commitments extend to all employees across every level of the company, encompassing both the corporate level and on-site operations. This applies to individuals working for Lithium Ionic on both a direct-employment and contractor basis. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe how the policy commitments are communicated to employees, business partners, and other relevant parties |
All employees must adhere to the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Embedding policy commitments | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe how the organization embeds each of its policy commitments for responsible business conduct throughout its activities and business relationships | ||||||||||||||||||
| How are responsibilities allocated in order to implement the commitments across different levels within the organization |
The Code of Business Conduct and Ethics outlines the principles of conduct for employees, officers, and directors of Lithium Ionic. The Corporation expects all its employees, officers, and directors to consistently comply with and adhere to the principles stated in the Code. |
|||||||||||||||||
| How are the commitments integrated into organizational strategies, operational policies, and operational procedures |
The Code comprehensively governs all facets of company operations, addressing key areas such as the workplace environment, third-party relationships, legal compliance, information and records, as well as company assets. It serves as a guiding framework to ensure adherence to ethical standards and responsible conduct across diverse aspects of the organization. |
|||||||||||||||||
| How does the organization implement its commitments with and through its business relationships |
The Code extends to third-party relationships, encompassing supplier-contractor engagements, public relations, and business and government interactions. This entails maintaining the company's integrity by avoiding conflicts of interest, bribery, and engaging in fair competition practices. |
|||||||||||||||||
| What implementation training does the organization provide |
While Lithium Ionic does not offer specific implementation training for its policies, individuals with questions regarding the contents of the policy are encouraged to seek advice from senior management or the board of directors. This approach ensures that employees have access to the necessary guidance and support to understand and adhere to the company's policies effectively. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Governance structure and composition | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe the composition of the highest governance body and its committees by: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Number of executive members (non-independent) | 4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of non-executive members (non-independent) | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of independent members | 4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Less than 3 years of tenure of members on the governance body | 8 | |||||||||||||||||
| 3-6 years of tenure of members on the governance body | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| 6-9 years of tenure of members on the governance body | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| More than 10 years of tenure of members on the governance body | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of other significant positions and commitments held by each member, and the nature of the commitments |
None of our board of directors members are active on more than five companies For a full description of each board member see attached link: |
|||||||||||||||||
| Board of Directors | ||||||||||||||||||
| Number of Male governance body members | 6 | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of Female governance body members | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of Non-Binary governance body members | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of Gender not disclosed governance body members | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of members from under-represented social groups | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
|
While our current board composition lacks visible minorities or members from under- represented social groups, we are committed to enhancing diversity and inclusion. One of our many goals is to increase the representation of women to more than 25% as the project progresses. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Description of competencies relating to economic, environmental, and social topics |
A description of each board member's experience and expertise can be found in the company description. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Board of Directors | ||||||||||||||||||
| Highest Governance Body | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe the nomination and selection processes for the highest governance body and its committees |
The Board currently has eight directors, and their terms will end when a new Board is elected at the Meeting. If elected, each director will serve until the next annual general meeting or until a successor is chosen, unless they resign or the position becomes vacant. To elect directors, a majority of votes at the Meeting is needed. Common Shares represented by proxies supporting Management nominees will be voted in favor unless the proxies specify otherwise. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Do you have a diversity policy and if so, provide details, link to the policy or attach the file |
Lithium Ionic does not maintain a separate diversity policy; instead, all diversity-related topics are encompassed within the broader framework of the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Code of Business Conduct and Ethics | ||||||||||||||||||
| Report the criteria used for nominating and selecting highest governance body members | ||||||||||||||||||
| Discuss whether and how views of the stakeholders (including shareholders) are involved |
The Board has the exclusive responsibility for finding new candidates for nomination. Candidates are identified through recommendations presented to the Board, which assesses qualifications in line with corporate law, regulatory requirements, and relevant education and experience related to the Corporation's business. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Chair of the highest governance body | ||||||||||||||||||
| Is the chair of the highest governance body also a senior executive in the organization (non-independent) | Yes | |||||||||||||||||
| If the chair is also a senior executive, explain their function within the organization’s management, the reasons for this arrangement, and how conflicts of interest are prevented and mitigated |
As detailed in the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, Lithium Ionic has implemented stringent guidelines and rules to prevent and safeguard against conflicts of interest. The Code mandates that employees, officers, and directors of the Corporation must conduct themselves with honesty and integrity, steering clear of any relationships or activities that could give rise to, or seem to give rise to, a conflict between their personal interests and the interests of the Corporation. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Conflicts of Interest | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe the processes for the highest governance body to ensure that conflicts of interest are prevented and mitigated |
The Code of Business Conduct and Ethics features a dedicated section addressing conflicts of interest, providing measures to prevent and mitigate any potential current or future conflicts. Additionally, an Anti-Bribery Policy has been implemented to specifically prevent corruption and acts of self-interest. In a commitment to transparency and independent judgment, the Board takes specific actions. This involves holding in-camera sessions with independent directors when necessary and requiring each director to declare their interest in a particular transaction. Directors are expected to abstain from voting on matters where their personal interest is involved, reinforcing the commitment to ethical governance and avoiding potential conflicts of interest. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Are conflicts of interest disclosed to stakeholders | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Are there conflicts of interest related to: cross-board membership | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Are there conflicts of interest related to: cross-shareholding with suppliers and other stakeholders | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Are there conflicts of interest related to: existence of controlling shareholder | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Are there conflicts of interest related to: related parties, their relationships, transactions, and outstanding balances | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Collective knowledge of highest governance body | ||||||||||||||||||
| Report measures taken to advance the collective knowledge, skills and experience of the highest governance body on sustainable development. (e.g. board training) |
The Board ensures new directors undergo an orientation education program covering duties, the Corporation's business, and recent Board meeting documents. Opportunities for meetings with senior management and other directors are also provided. Highlighting the ongoing importance of director education, the Board emphasizes each director's personal responsibility. Valuing members' experience in navigating evolving governance principles, the Board commits to leveraging their expertise for insights and fostering continuous improvements, especially in sustainable development |
|||||||||||||||||
| Evaluation of Highest Governance Body | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe actions taken in response to the evaluations, including changes to the composition of the highest governance body and organizational practices |
The Board and individual directors undergo continuous informal assessments of their effectiveness and contribution. The Chairman encourages discussions within the Board for evaluating both the overall effectiveness of the Board and the performance of each director. All directors are encouraged to share suggestions for improving the Board's practices at any time. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Transparency | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe the role of the highest governance body and of senior executives in developing, approving and updating the organization’s purpose, value or mission statements, strategies, policies and goals related to sustainable development |
Lithium Ionic is guided by a set of core values - safety, integrity, responsibility, accountability, and excellence. These principles not only shape the current operational framework but also play a crucial role in formulating future policies related to sustainable development. By embedding these values in all aspects of its operations, the company remains dedicated to a foundation of ethical and responsible business practices. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe the role of the highest governance body in overseeing the organization’s due diligence and other processes to identify and manage the organization’s impacts on the economy, environment and people |
Senior management at Lithium Ionic maintains regular communication with both on-site and corporate-level employees to ensure compliance with all relevant regulations. Additionally, senior management conducts site visits to verify that operations are conducted safely and in adherence to all required laws and frameworks. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe whether and how the highest governance body engages with stakeholders to support these processes |
The Corporation has adopted a Majority Voting Policy, providing a meaningful mechanism for shareholders to hold individual directors accountable. This policy requires the Corporation to review directors who fail to secure the support of a majority of shareholders. As per the policy, proxies for director elections enable shareholders to express their votes individually for or against each director nominee. If a director nominee receives more votes against them than in favor, they will not be considered to have obtained shareholder support. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Ethics | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ethics and Integrity | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe how individuals can seek advice on implementing the organization’s policies and practices for responsible business conduct |
Individuals seeking advice on implementing the organization's policies and practices for responsible business conduct can seek guidance from the CEO, President, COO, CFO, or Corporate Secretary. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe the mechanisms for individuals to raise concerns about the organization’s business conduct |
Lithium Ionic is in the process of developing a grievance mechanism to facilitate a more accessible communication channel within the hierarchy of operations for expressing concerns related to the organization's business conduct. In the interim, individuals are encouraged to raise any concerns they may have, with senior management or members of the board. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Compliance with laws and regulations | ||||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of significant instances of non-compliance with laws and regulations that occurred during the reporting period and a breakdown of this total by | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Lithium Ionic reaffirms its commitment to compliance with all applicable laws and regulations governing operations in Brazil and Canada. Currently, the organization has not experienced any instances of non-compliance and continues to adhere to the required legal standards. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Number of instances for which fines were incurred | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of instances for which non-monetary sanctions were incurred | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Report the total number of fines for instances of non-compliance with laws and regulations that were paid during the reporting period | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe the significant instances of non-compliance | N/A | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe the management system and due diligence procedures for assessing and managing corruption and bribery risks internally and associated with business partners in its value chain |
Lithium Ionic has implemented a comprehensive Anti-Bribery policy, affirming a steadfast commitment to comply with all anti- bribery and anti-corruption laws in every jurisdiction where the company operates or has a presence. The policy prohibits all directors, officers, employees, and external parties acting directly or indirectly on behalf of the company from engaging in bribery or any corrupt activity, whether in connection with government officials or private parties, as well as from enabling or facilitating such activities. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Anti-Corruption | ||||||||||||||||||
| Confirmed Incidents and Response | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total number and nature of confirmed incidents of corruption | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of Bribery cases | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of Lobbying cases | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of Extortion cases | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of Cronyism cases | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of Nepotism cases | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of Parochialism cases | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of Patronage cases | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of Influence peddling cases | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of Graft cases | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of Embezzlement cases | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of confirmed incidents in which employees were dismissed or disciplined for corruption | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of contracts terminated or not renewed with business partners due to corruption related violations | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of public legal cases brought against the organization or its employees during the reporting period related to corruption and the outcomes of such cases | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Provide details, if there were such public legal cases brought against the organization or its employees during the reporting period related to corruption and the outcomes of such cases | N/A | |||||||||||||||||
| Communication and Training | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of governance body members that the organization's anti-corruption policies and procedures have been communicated to | 8 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Our Anti-Bribery Policy and Code of Business Conduct and Ethics apply to all members within our organization, including those comprising the governance body. Members of our board are fully briefed on these policies and are obligated to uphold the principles outlined therein. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total percentage of governance body members that have been communicated to on anti-corruption | 100.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Total number of governance body members that have received training on anti-corruption | 8 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Every member of the governance board is mandated to comply with and have full awareness of their obligations under the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, as well as the Anti-Bribery Policy. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total percentage of governance body members that have received training on anti-corruption, broken down by region | 100.0000% | |||||||||||||||||
| Communication of critical concerns | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe whether and how critical concerns are communicated to the highest governance body |
Critical concerns are communicated to the board of directors through channels facilitated by the CEO, President, COO, CFO, or Corporate Secretary. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Report the number of critical concerns that were communicated to the highest governance body during the reporting period | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Report the nature of critical concerns that were communicated to the highest governance body during the reporting period |
No critical concerns were communicated to the highest governance body during the reporting period. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Remuneration | ||||||||||||||||||
| Report which of the following remuneration policies apply to the highest governance body and senior executives: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed pay | Yes | |||||||||||||||||
| Variable pay | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Performance-based pay | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Equity-based pay | Yes | |||||||||||||||||
|
Equity-based pay is available through stock options |
||||||||||||||||||
| Bonuses | Yes | |||||||||||||||||
| Deferred and vested shares | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Sign-on bonuses | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Recruitment incentive payments | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Termination payments | Yes | |||||||||||||||||
| Clawbacks | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Retirement benefits, including the difference between benefit schemes and contribution rates for the highest governance body, senior executives and all other employees | No | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe how the remuneration policies for members of the highest governance body and senior executives relate to their objectives and performance in relation to the management of the organization’s impacts on the economy, environment and people |
The Corporation's compensation plan for officers and consultants is designed to align with organizational goals, motivating individuals to meet or exceed corporate objectives and boost shareholder value. Executive compensation includes base salary, additional benefits, and long-term incentives like stock options. The actual compensation considers various factors, aiming for a balanced approach. It is set to be competitive in the market and reflects the responsibilities of each position, ensuring internal equity. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Describe the process for designing its remuneration policies and for determining remuneration |
The Board is responsible for deciding the compensation for the Corporation's directors and regularly reviews this compensation throughout the year. Directors who are not Named Executive Officers may receive stock options under the Stock Option Plan for their directorial role. No additional arrangements exist for compensating these directors for their services as directors of the Corporation or its subsidiaries during the most recently completed financial year end. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Are independent members of the highest governance body or an independent remuneration committee overseeing the remuneration process | Yes | |||||||||||||||||
| Describe whether remuneration consultants are involved in determining remuneration and, if so, whether they are independent of the organization, its highest governance body and senior executives | Independent Consultants | |||||||||||||||||
| Stakeholder Engagement | ||||||||||||||||||
| Report the purpose of the stakeholder engagement |
Lithium Ionic has proactively engaged in a series of community consultations as part of our ongoing commitment to thoroughly understand and align community expectations with the operational framework of LTH. These consultations are conducted in collaboration with Neo Agro Ambiental, a respected local environmental entity specializing in community engagement and consultation processes. The primary goal of these consultations is to establish a sustained dialogue with the local community. Through these interactions, we aim to gain a deeper understanding of their perspectives and concerns. This valuable insight is then incorporated into our decision- making processes and future programming. This approach is a key element of our corporate strategy, facilitating the alignment of our operations with the community's needs and expectations and fostering a stronger and more mutually beneficial relationship between our operations and the local community. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Tax | ||||||||||||||||||
| Describe the approach to stakeholder engagement and management of stakeholder concerns related to tax, including | ||||||||||||||||||
| The approach to engagement with tax authorities |
Lithium Ionic receives third-party expertise on tax-related issues and ensure full compliance with tax obligations. |
|||||||||||||||||
| The approach to public policy advocacy on tax |
Lithium Ionic does not currently have any approach to public policy advocacy on tax nor do we contribute any political donations in any country of operation. |
|||||||||||||||||
| The processes for collecting and considering the views and concerns of stakeholders, including external stakeholders |
Lithium Ionic frequently engages with stakeholders and addresses concerns as they are mentioned. |
|||||||||||||||||
| , Planet Earth's complete ESG reporting solution. | ||||||||||||||||||
